SunFed Ranch Grassfed Livestock Standards are written by and for producers, to support American family ranchers, and to provide a fair and sustainable market for their premium products which are better for the consumer, better for the earth, and better for the animal.
SunFed Ranch is dedicated to sourcing the healthiest and most environmentally beneficial grassfed beef by selectively promoting and supporting USA ranchers who raise 100% grassfed beef per SunFed Ranch standards. Accordingly, SunFed Ranch will always adhere to the following set of attributes:
All livestock entering the SunFed Ranch program must be fully documented and have traceability to birth. Adherence to SunFed Ranch standards and protocols will be controlled by SunFed Ranch and certified by stringent third-party and in-house Program Audits.
At SunFed Ranch, we believe that grassfed beef done right – raised with care, provided proper nutrition, integrated into restorative land management practices, harvested humanely and cleanly – will provide health benefits to our consumers, will promote sustainability and resilience for our ranchers, improve cattle health, and help reverse climate change. These protocols are the basis for our definition of “doing grassfed right.”
SunFed Ranch Best Practices are required to ensure the highest level of integrity regarding land, animal, ecosystem, and environmental management.
SunFed Ranch livestock breeds must be suited to the climate, geography, soil type and natural environment of the farm/ranch on which they are raised. Predominantly English Breed Cattle (Angus, Red Angus, Hereford, etc…) are preferred, no Bos Indicus or Dairy Cattle are allowed.
Low stress animal handling is always required. Animal handlers should demonstrate training in low stress stockmanship techniques that produce low stress to the animals and the handlers. Livestock must be allowed to express their instinctive behaviors.
Farm Plan: SunFed Ranch requires that every farming/ranching operation develop and maintain a Farm Plan. This plan serves as a central repository for all records, checklists, land management practices, water management practices, restorative agricultural practices, maps, pest control methods, standard operating procedures, emergency procedures, and internal policies. The farm plan should include clear practices for measuring and tracking soil health, specifically encompassing soil organic matter content, water infiltration, and biological activity and diversity. This Farm Plan shall be made available for review to SunFed Ranch as requested and reviewed annually by SunFed Ranch.
Restorative Agricultural Practices: Restorative agricultural practices implemented through grazing must be documented in the Farm Plan. Actively and intentionally managing grazing practices is key to quality grassfed beef both for cattle health and continuous ecological improvement. Rotational grazing, as compared to continuous grazing, mimics historical herd movements driven by forage timing and predator activity and is required within the SunFed Ranch system. Within this, concentrated herds are observed grazing pasture more uniformly for a limited period, before moving to new pasture. This pattern allows for optimal plant/forage generation, regeneration, and soil health. Pasture managed via rotational grazing increases yields and soil vitality, all while reducing need for additional fertilizers and external inputs.
Soil health is the basis of restorative agriculture. To distill the science, we follow The Five Principles of Soil Health, as detailed by Jay Furher, NRCS Soil Health Specialist:
The Five Principles of Soil Health
Principle 1: Maintenance of soil armor/soil cover
Principle 2: Minimization of soil disturbance
Principle 3: Promotion of plant diversity
Principle 4: Continual live plant/root
Principle 5: Livestock integration
Stocking rates must be appropriate and tied to the soil, climate, and geography of the farm/ranch. Pasture management and grazing plans minimize animal concentration areas by moving supplemental feed areas and placement of mineral. Pastures must be managed to minimize or eliminate the use of synthetic fertilizers, herbicide, and pesticides. Existing riparian areas must be protected and maintained.
The Language Used in the Standards. These words are used to convey requirements for specific standards within the SunFed Ranch Grassfed System.
Cattle Certification Program:
All required records must be in sufficient detail as to demonstrate compliance with SunFed Ranch standards to the inspector, auditor, or inspection agency and retained for three (3) years.
Records must be kept demonstrating all SunFed Ranch Grassfed Market animals are raised to SunFed Ranch’s Grassfed Standards from birth to harvest for three (3) years.
All livestock production must be pasture/grass/forage based.
Grass and forage must be the feed source consumed for the lifetime of the cattle, except for milk consumed prior to weaning. The diet must be derived solely from forage appropriate to the livestock requirements:
a) Grass (annual and perennial)
b) Forbs (e.g., legumes, brassicas)
c) Browse
d) Cereal grain crops harvested in the pre-dough stage
e) Harvested forages
All SunFed Ranch Grass-fed cattle must be provided maximum access to pasture and must optimize their dry matter intake grazed from pasture during the grazing season except during:
a) Roundups
b) Sorting
c) Weaning
d) Transportation
e) Nighttime confinement
Pastures must provide forage, in sufficient quality and quantity, and to maximize grazing for grass-fed cattle during the grazing season. See “grazing season” in definitions.
Feeding SunFed Ranch cattle animals in confinement or a Concentrated Animal Feeding Operation (CAFO) is prohibited. CAFO is defined as agricultural facilities that house and feed a large number of animals in a confined area for 45 days or more during any 12-month period.
All farms/ ranches will have in place a written pasture management and grazing plan that supports biological diversity, natural resources, and building of soil fertility.
The use of synthetic herbicide and pesticide is prohibited with these exceptions:
a) Weeds and invasive plants or pests have not been effectively controlled using other sustainable/holistic means.
b) Prescriptive individual plant treatment (IPT) of herbicide to remove invasive plant species.
SunFed Ranch Grassfed cattle may only be removed from pasture during inclement weather or events that may threaten the health, safety and welfare of the cattle, natural resources or when conditions compromise the ability to graze.
SunFed Ranch Grassfed cattle removed from pasture must have access to the outdoors unless conditions jeopardize the health, safety and welfare of the cattle or there is a risk of damaging soil structure due to wet soil conditions. Sacrifice pastures are permissible to protect surrounding pastures from overuse during extended inclement weather conditions or times of slow pasture re-growth (drought).
Grazing of harvested grain fields is permitted, if 75% of the field is in vegetative re-growth and the average height of the re-growth is 8”.
SunFed Ranch Grassfed cattle may receive supplemental feed or nutritional supplements on pasture or as necessary. Approved supplements include:
a) hay & haylage
b) balage
c) silage*
d) forage products*
e) crop residue without grain
f) small grains harvested in the pre-dough stage
g) roughage*
*See Definitions
SunFed Ranch Grassfed livestock must receive a balanced diet, including protein, energy, minerals, and vitamins and be appropriate to the animals age and stage of production.
SunFed Ranch Grassfed Market animals may be fed approved supplements to ensure the animal’s well-being during periods of low forage quality or inclement weather.
The feeding of forage products and supplemental feedstuffs to SunFed Ranch Grassfed Market animals not listed in Appendix A, Approved SunFed Ranch Forage Products and Supplement Feedstuffs, is prohibited.
Feeding of approved forage products and supplemental feedstuffs to SunFed Ranch Grassfed Market animals must comply with the feeding guidelines in Appendix A.
Intentional feeding of grain or prohibited feeds & ingredients in Appendix C to SunFed Ranch Grassfed market animals is prohibited and will cause loss of Certified Grassfed status.
Mineral and vitamin supplements, with no cereal grain carriers, may be provided free choice, or may be mixed into supplemental forage feed to adjust the animal’s nutrient intake and to correct deficiencies in its total diet.
A log of supplemental feedstuffs fed to SunFed Ranch Grassfed market animals must be kept including type of supplement, timing and amounts fed. Log must be provided to SunFed Ranch and kept on location for three (3) years.
All livestock production methods and management practices must promote animal health and welfare, expression of natural behavior, safety, low stress handling, transport and humane slaughter.
Producers must have a written herd health plan, either in consultation with a veterinarian updated every two years; or participate in an ongoing third-party animal welfare program that includes on-farm visits.
Living conditions for all livestock must accommodate the health and natural behaviors of the animals. Shade, shelter, fresh air and clean drinking water must be provided daily for animals. Pastures, fields, and shelter must be large enough to allow all animals to graze/feed without crowding or competition for food.
Electric cattle prod use is prohibited except in instances to prevent risk of injury to the animal or handler.
SunFed Ranch Grassfed Market animals must not be fed or treated with antibiotics except as prescribed in their respective herd health plans under veterinary supervision. Treated animals will lose their Certified Grassfed status. Sick or injured Grassfed market animals must be treated to relieve symptoms. Animals must not be treated with prohibited medications.
If SunFed Ranch Grassfed market animals are treated with prohibited medications to comply with the herd health plan, the animal must be permanently identified at time of treatment with an ear tag, notched dangle tag or other clear and visual form of separation to designate that they no longer qualify for SunFed Ranch Grassfed program.
SunFed Ranch Grassfed market animals treated with prohibited medications must be tracked. Records must be kept demonstrating that meat from treated animals does not enter the SunFed Ranch Grassfed Program. Provided the identification and tracking comply with the above standard, the animal may still be kept with other cattle that qualify for SunFed Ranch Grassfed certification and must be excluded from the SunFed Ranch supply chain.
The producer must develop and maintain a written record of all vaccines, medications, or other substances used in his/her animal health care program. Records must be provided to the inspector/inspection agency and maintained for three (3) years.
The producer must keep receipts for all antibiotics administered. Antibiotic receipts and records of use must be available on demand to the inspector/inspection agency.
If pasture management or sustainable/holistic alternatives to control worms, lice or other parasites is ineffective synthetic endectocide may be used with SunFed Ranch approval.
SunFed Ranch Grassfed market animals fed or treated with any products in Appendix B is prohibited and will cause loss of animal’s Certified Grassfed status.
The use of organophosphates, beta agonists or ionophores, or any product containing these where an animal might ingest or absorb them, is prohibited for SunFed Ranch grassfed market animals, and will cause the loss of the animal’s SunFed Ranch Grassfed status.
Genetically modified or cloned animals are prohibited. Embryo transfer livestock must meet stringent guidelines and be approved by SunFed Ranch before placement into the SunFed Ranch system.
SunFed Ranch Grassfed market animals must be born and raised in the USA.
SunFed Ranch Grassfed market animals must be traceable by written record throughout their entire lives from birth to harvest. Complete and up-to-date records must be maintained to identify all animals raised, purchased, sold, and harvested as part of the SunFed Ranch Grassfed cattle program.
Each producer must develop and maintain an animal identification system to identify each animal or batch of animals approved by SunFed Ranch.
Grassfed cattle take longer to mature and achieve optimal weight than cattle raised in confined feeding operations. Accordingly, we target harvest when cattle are between 24 and 30 months of age.
All Source and age records are to be maintained for at least three (3) years after the animal is sold or harvested.
SunFed Ranch Grassfed Cattle: Any cattle animal raised in a SunFed Ranch Grass-fed production system.
Grass-fed cattle perform best when provided a steady plane of nutrition allowing them to grow healthily and consistently. Genetics, quality of feed/forage, environmental conditions and seasonality all play into determining appropriate fat cover on an animal.
Producers in this program will use a scoring method to monitor and document body condition of the cattle to focus attention on animal health and wellbeing.
The broadly utilized Beef Cattle Body Condition Scoring (BCS) is based around a 1-9 scoring legend outlined as follows:
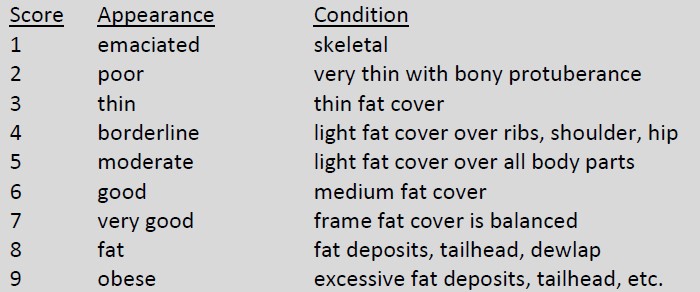
A score of 3 or higher is required for participation in the SunFed Ranch program, with a score of 5-7 being appropriate for grassfed cattle at time of harvest. Cattle with a BCS of 1 or 2 are considered mal-treated/mal-nourished and fall outside the parameter set forth within the SunFed Ranch Cattle Welfare Standards. Individual animals with a BCS of 1 or 2 shall receive veterinary attention and may be reintroduced to the program per veterinary recommendation. Observation of cattle with BCS 1-2 in over 30% of the herd signals mishandling or maintenance of inappropriate conditions for cattle and will result in suspension from the SunFed Ranch program.
Balage or Round Bale Silage: A practice that involves cutting the forage crop with conventional hay harvesting equipment, allowing the forage to wilt to between 30 and 60 percent dry matter, then baling it into tight bales and wrapping them immediately. Bales are wrapped mechanically using bale-wrapping equipment that tightly stretches several layers of plastic around the hay to exclude oxygen and allow proper ensiling.
Boot Stage (Grain): The flag leaf is fully expanded, but the awns and grain head are not visible. The grain head can be felt in the flag leaf sheath.
Brassicas: A family of very productive annual forage vegetables used as transition crops between pasture renovations or as a supplemental feed source for extending the grazing season when other forages are less productive, examples include turnips, rape, and kale.
Browse: 1) Leaf and twig growth of shrubs, woody vines, trees, cacti, and other non-herbaceous vegetation available for animal consumption.
Commercially Available: The ability to obtain a product in an appropriate form, quality or quantity.
Crop Residue: Portion of plants remaining after fruit and/or seed harvest, said mainly of grain crops such as corn stover or of small grain straw and stubble.
De Minimis: Amount too trivial or minor to merit consideration, <1.5%.
Diet: The feed regularly offered to or consumed by an animal, see ration.
Dough Stage: The kernel is filled with starch and is well formed. There is no milky fluid, only a rubbery, dough-like substance.
Dormancy: In a state of being dormant when no active growth is occurring.
Enticement: A feedstuff used with management practices but is not a part of the overall animal ration
Ensiled: Having been subjected to anaerobic fermentation to form silage.
Extenuating circumstances: include but are not limited to barn fire, family emergencies, federal or state mandated conditions, etc.
Family Farm: SunFed Ranch defines a Family Farm as a farm in which the farm owners own the animals and are responsible for all management decisions regarding operation of the farm/ranch.
Feedstuff: The constituent forages, feeds, or supplements of an animal ration.
Forage: any herbaceous plant material that can be grazed or harvested for feeding, except for grain. Including small grains harvested or grazed in the pre-dough stage.
Forage Products: Products derived exclusively from forage.
Forb: Any herbaceous broadleaf plant that is not a grass and is not grass-like.
Fruit: 1) n. The usually edible reproductive body of a seed plant, one having a sweet pulp associated with the seed.
Genetically modified organism: many methods used to influence the growth or development of organisms by means that are impossible under natural conditions or processes. Such methods include cell fusion, microencapsulation and macro encapsulation, recombinant DNA technology (including gene editing, gene deletion, gene doubling, introducing a foreign gene, and changing the position of genes when achieved by recombinant DNA technology). Such methods do not include the use of traditional breeding, conjugation, fermentation, hybridization, in vitro fertilization, or tissue culture.
Grain: Seed from cereal plants, caryopsis. Corn, wheat, rye, oats, rice, millet, sorghum, barley, triticale.
Grass: Member of the plant family Poaceae.
Graze: 1) the consumption of standing or residual forage by livestock; 2) to put livestock to feed on standing residual forage
Grazing Season: The period when pasture is available for grazing, due to natural precipitation or irrigation.
Growing Season: The number of days between the last spring freeze date and the first fall freeze date.
Hay: The aerial parts of forage crops stored in the dry form for animal feeding.
Haylage: Haylage is the feed produced by storing a forage crop, dried to a moisture level of about 45-55% in an airtight silo.
Herbage: 1.) The biomass of herbaceous plants, other than separated grain above ground but including edible roots and tubers. 2.) n. Green plants especially when used or fit for grazing.
Hydrolysis: The splitting of a substance into the smaller units by its chemical reaction with water.
Inclement Weather: Weather that is violent, or characterized by temperatures (high or low), or characterized by excessive precipitation that can cause physical harm to a species of livestock.
Production yields or growth rates of livestock lower than the maximum achievable do not qualify as physical harm
Kernel: A mature ovule of a grass plant with the ovary wall fused to it. Same as caryopsis.
Legumes: Members or the Fabaceae plant family (formerly known as the Leguminoseae family). Legumes are dicots (produce two seed leaves), produce seed in a pod, have netted leaf venation, and usually have a taproot type of root system. Most legumes can interact with bacteria of the genus Rhizobium to fix nitrogen in nodules on their roots. Legumes may have one of four types of seed heads. These seed head types are the raceme, the spike, the head, or umbel.
Meadow: Area covered with grasses and/or legumes, often native to the area, grown primarily for hay but with secondary grazing potential.
Milk Stage: Initial phase of grain development, after the flowering stage. In corn, the R3 stage. About 18 to 22 days after silking, when the kernels are mostly yellow and contain “milky white fluid.
Mineral: 1) n. a solid homogeneous crystalline chemical element or compound that results from the inorganic processes of nature. 2) n. The various naturally occurring homogeneous substances obtained usually from the ground. 3) n. a synthetic substance having the chemical composition and crystalline from and properties of a naturally occurring mineral.
Native Pasture: Native vegetation (predominantly herbaceous) used for grazing in untilled areas. The term tame or introduced is used instead of native for pastures that include mainly nonnative species.
Natural Resources of the Operation: The physical, hydrological, and biological features of a production operation, including soil, water, wetlands, woodlands, and wildlife.
Nighttime Confinement: Collecting of animals from dusk until dawn in a fenced enclosure, generally utilizing temporary electric fence or a designated sacrifice area, to keep animals protected from predators.
Non-fibrous carbohydrate (NFC): The fraction of a feedstuff made of sugars and starch.
Paddock: A grazing area that is a subdivision of a grazing management unit and is enclosed and separated from other areas by a fence or barrier.
Pasture: 1) n. Forages harvested by grazing animals. 2) n. An area of land with 75% forage cover or unbroken land on which livestock may graze at will.
Pasture-based: Land management systems where livestock are raised on pasture and allowed to graze freely and express their natural behaviors.
Pastureland: Land devoted to the production of indigenous or introduced forage for harvest primarily by grazing. Pastureland must be managed to arrest succession processes.
Pericarp: The ripened and variously modified walls of a plant ovary, especially those contributing the outer layer in a cereal caryopsis.
Prairie: Nearly level or rolling grassland originally treeless; usually characterized by fertile soil.
Range: Land supporting indigenous vegetation grazed or that has the potential to be grazed and is managed as a natural ecosystem. Includes graze able forestland and rangeland.
Rangeland: land on which the indigenous vegetation (climax or natural potential) is predominantly grasses, grass-like plants, forbs, or shrubs suitable for grazing or browsing use and is managed as a natural ecosystem. If plants are introduced, they are managed as indigenous species.
Rangelands include natural grasslands, savannas, shrub lands, most deserts, tundra, alpine communities, coastal marshland, and wetland meadows.
Ration: the total feedstuffs (diet) allotted to one animal for a 24-hour period.
Residue: that which remains of any substance.
Roughage: Any feed ≥ 18% in crude fiber and ≤ 70% in total digestible nutrients (TDN), on an airdried basis and are less than 5.5% crude fat.
Sacrifice pasture: A pasture where animals may move about and express their natural behaviors and where forage can be grown during the grazing season.
Seed: 1) n. Ripened mature ovule comprising an embryo, a seed coat, and a supply of food that, in some species is stored in the endosperm. 2) v. To sow, broadcast or drill small-seeded grasses, legumes, or other crops.
Seed head: See inflorescence.
Separated Grain: Grain detached from cereal crop plants.
Silage: Silage, as defined by SunFed Ranch, is forage harvested in the pre-dough stage of grain formation.
Soil and Water Quality: Observable indicators of the physical, chemical, or biological condition of soil and water, including environmental contaminants.
Starch: A polysaccharide having the formula (C6H10O5). Many plants store energy in starch. Starch is a major component of most livestock rations (especially fattening rations) and is highly digestible. Yields glucose upon complete hydrolysis.
Stockpiled Forage: Forage allowed to accumulate on a pasture or paddock for grazing at a later period. Forage is often stockpiled for autumn and winter grazing after or during dormancy or semi dormancy, but stockpiling may occur during the year as a part of a forage management plan. Stockpiling can be described as forage accumulation.
Stover: The matured cured stalks of such crops as corn or sorghum from which the grain has been removed.
Stubble: The basal portion of the stems of herbaceous plants left standing after harvest.
Supplement: A nutritional additive (salt, protein, phosphorus, etc.) intended to improve the nutritional balance and remedy deficiencies of the diet.
Supplemental Feeding: The practice of supplying feedstuffs to correct nutritional deficiencies in an animal’s “natural” diet.
Vegetative: Non-reproductive plant parts, (leaf and stem) in contrast to reproductive plant parts (flower and seed) in developmental stages of plant growth. The non-reproductive stage in plant development.
Vegetative State: Stage prior to the appearance of fruiting structures.
Vitamin: Any of various organic substances essential in minute quantities to the nutrition of most animals and some plants that act especially as coenzymes and precursors of coenzymes in regulating metabolic processes
Note: SunFed Ranch Supplement Guidelines apply to SunFed Ranch Grassfed market animals and do not apply to breeding animals unless breeding animals will be marketed through the SunFed Ranch Grassfed cattle.
When supplements are used, it seems logical these supplements should be looked upon as substitutes or replacements for the pasture that is not available. The supplements should be nutritionally comparable in the major nutrient content of the forage being replaced. The nutrients considered should be uniformly available (nutritionally speaking) and include energy, fiber, nonfibrous carbohydrate (NFC) and protein. Since most pasture grasses, legumes and mixtures contain 20% to 30% NFC, it seems axiomatic that supplements should contain levels of NFC along with a high level of highly digestible fiber. This rational is that the NFC percentage along with the fiber content is an acceptable criterion for judging of supplemental feedstuffs. The goal of any supplementation would be to not change the nutrient profile of the meat product produced while ensuring that the daily nutritional requirements of the animal is met.
Feeds or ingredients with an adverse effect on the nutritional quality or have negative health benefits on the animals fed will not be allowed.
Bio Supportive Supplements:
a. Kelp
b. Algae
c. Apple cider vinegar
Molasses Products:
a. Sugar Products or Molasses Products may be fed up to 4 lbs./head/day on a dry matter basis as an energy source during the non-growing season or periods of low forage quality.
b. molasses Products may be a carrier in mineral or vitamin blocks and tubs. It may be used as a binder or ingredient in pellets or cubes.
Molasses Protein Tubs:
SunFed Ranch Grassfed cattle may be supplemented with molasses-based protein blocks or tubs to maintain nutrient and rumen balance during periods of low forage quality and inclement weather if these conditions are met:
a) The block or tub must list a targeted daily intake of 3 pounds or less. (Chemically hardened or cooked blocks/tubs)
b) The block or tub may use approved plant protein products.
c) The ingredient tag must not list any Banned Products listed in Appendix B.
d) The ingredient tag must not list prohibited Ingredients in Appendix C.
Note: Any tub or block that lists protein % first on its guaranteed analysis tag is considered a protein tub.
Manufactured Feeds, Cubes, Pellets:
SunFed Ranch Grassfed cattle may be fed approved feeds, cubes, or pellets to ensure the animal’s wellbeing during periods of low forage quality or inclement weather or as an enticement during sorting, round up and pasture rotation if these conditions are met:
a) Manufactured feed that list approved Forage Products, Roughage Products or Plant Protein Products.
b) Amount fed not to exceed 0.625% of body weight per day (25% total daily intake) and 1% of lifetime intake when calculated on a dry matter basis.
c) The ingredient tag must not list any Banned Products listed in Appendix B.
d) The ingredient tag must not list prohibited Ingredients in Appendix C.
SunFed Ranch Plant Protein Products:
Approved protein products may be ingredients in a ration or manufactured product. SunFed Ranch approved plant protein Products must be ≤ 30% NFC.
Note: Producers may request the SunFed Ranch to evaluate Forage Products and Supplemental Feedstuffs not listed in Appendix A for approval. Supplements with an adverse effect on the nutritional quality of the meat produced or have negative health benefits on the animals fed will not be permitted.
Note: Producers may request a temporary variance from the quantity restrictions for approved forage products and supplement feedstuffs when confronted with extended inclement weather conditions.
Feeding or administering the products listed below to SunFed Grassfed Cattle will cause loss of Grassfed Certification status.
a. Antibiotics
b. Growth promoters
c. Feather Meal
d. Animal by-products
e. Milk replacer containing antibiotics, growth promoters and/or any animal by-products aside from whey and other dairy products are not allowed.
The following list of prohibited ingredients and feeds is not an exclusive list. SunFed Ranch may review and amend this list periodically. Grain products or processed grain products in any form such as whole, ground, cracked, flaked, silage, distilled (distiller grains) or toasted are prohibited.
a. Barley
b. Corn
c. Oats
d. Rye
e. Rice
f. Triticale
g. Wheat
h. Millet
i. Sorghum
j. Soy protein products
k. Urea
l. Sunflower meal
SunFed Ranch engages with professionals throughout multiple segments of the industry to ensure the latest information on grassfed systems, humane handling, and restorative agricultural practices are available to program participants. Regular revision of the SunFed Ranch Cattle/Beef Protocols and additional training presented to program participants is often based on new developments in health, nutrition, humane handling, and agricultural developments offered to SunFed Ranch by outside professional advisors and industry experts.
Colorado State University College of Agricultural Sciences: https://agsci.colostate.edu/
Humane Farm Animal Care (Certified Humane®): https://certifiedhumane.org/
The Savory Institute: https://savory.global/
North American Meat Institute: https://www.meatinstitute.org/
Non-GMO Project: https://www.nongmoproject.org/
The Carbon Underground: https://thecarbonunderground.org/